Clinical Trials for Patients Age 6 Years or Older
TRIAL 2 (ENVISION): Patients with CF age 6 to <11 with a G551D mutation. KALYDECO® (ivacaftor): Efficacy results include significant improvement in lung function1,2
ON THIS PAGE: Study Design | Summary of Results
Mutation Eligible for Study1 (mutation in bold was enrolled)
G551D
STUDY DESIGN1
- Trial 2 was a 48-week, Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (N=52) in patients with CF age 6 to 11 years (mean age: 9 years) and a G551D mutation
- Patients had to have FEV1 40%-105% predicted at screening [mean FEV1 84% predicted at baseline (range: 44%-134%)]
- Patients received KALYDECO 150 mg or placebo every 12 hours with fat-containing food, in addition to their prescribed CF therapies. Use of hypertonic saline was not permitted
Primary endpoint1: Improvement in lung function as determined by the mean absolute change from baseline in ppFEV1 through Week 24
Other efficacy endpoints2: Absolute change in ppFEV1 through Week 48, improvement from baseline in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score through Weeks 24 and 48, absolute change from baseline in body weight at Weeks 24 and 48, and absolute change from baseline in sweat chloride concentration through Weeks 24 and 48
SUMMARY OF RESULTS1,2
Improvements in ppFEV1 vs placebo were seen at the first post-baseline visit and persisted through 48 weeks1,2
Treatment difference through:
24 weeks (primary endpoint)1,2,a
+12.5 points
(95% CI: 6.6, 18.3; P<0.0001)
48 weeks (secondary endpoint)1,2,a
+10.0 points
(95% CI: 4.5, 15.5; P<0.001)
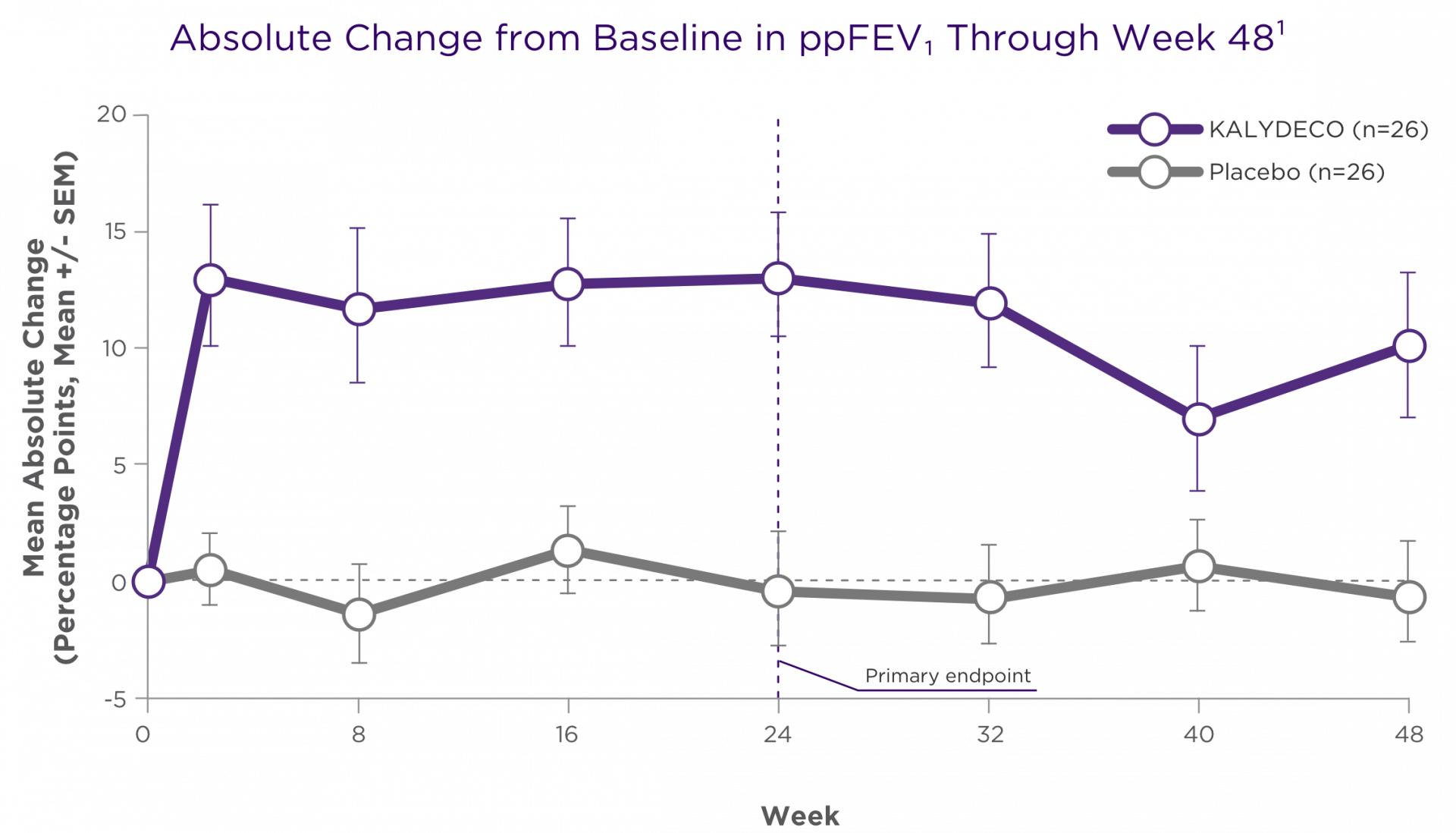
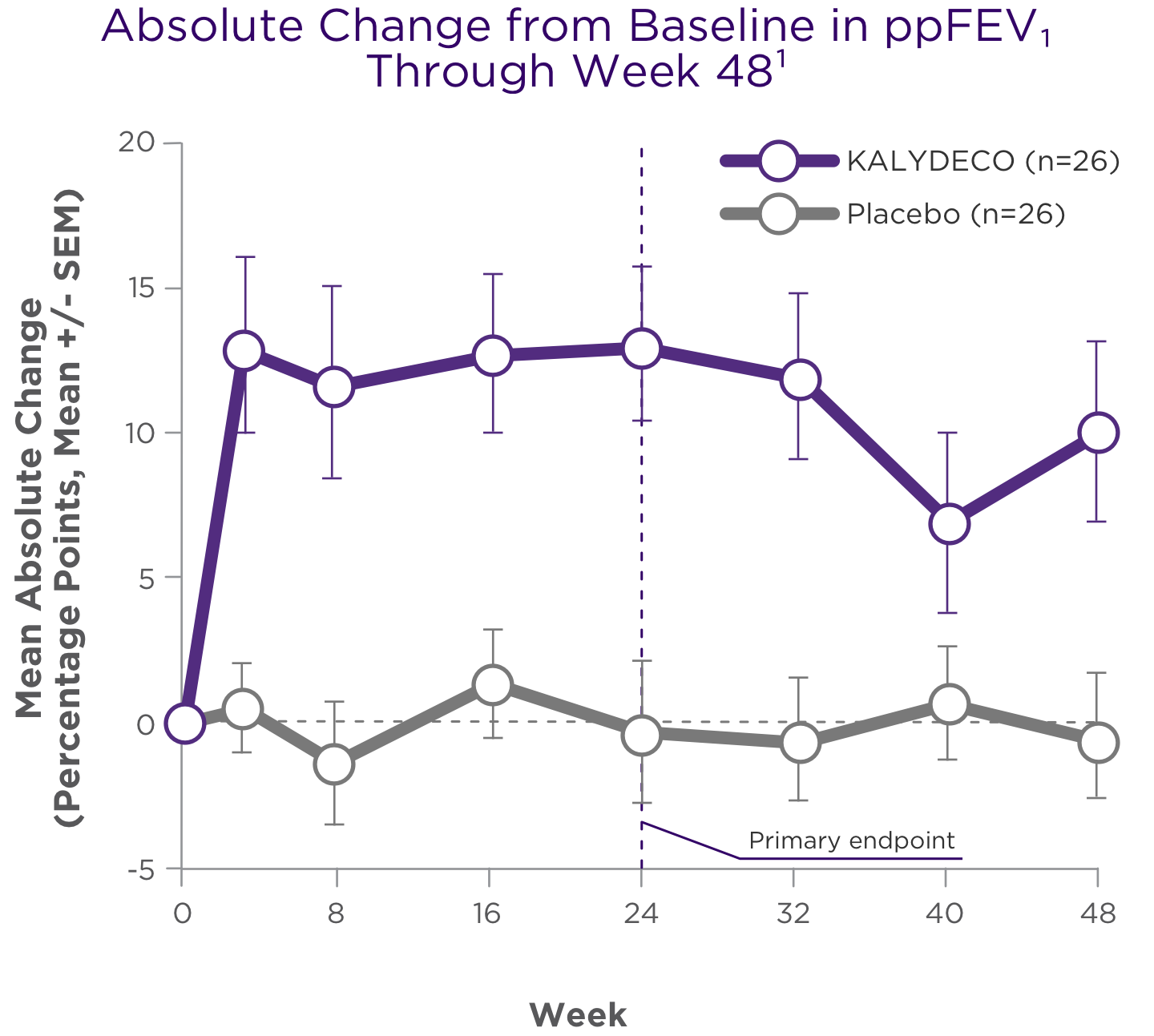
aTreatment difference = effect of KALYDECO – effect of placebo.1
Primary endpoint was assessed through 24 weeks for Trial 2 and was based on a mixed-effects model for repeated measures (MMRM).1,2
CFQ-R, Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Other efficacy endpoints1
CFQ-R RESPIRATORY DOMAIN SCORE
Treatment difference through:
24 weeksa
+6.1 points (95% CI: -1.4, 13.5; not statistically significant)
48 weeksa
+5.1 points (95% CI: -1.6, 11.8; not statistically significant)
- CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score evaluated relevant CF respiratory symptoms, including cough, sputum production, and difficulty breathing1
BODY WEIGHT
Treatment difference at:
24 weeksa
+1.9 kg (95% CI: 0.9, 2.9; P=0.0004)
48 weeksa
+2.8 kg (95% CI: 1.3, 4.2; P=0.0002)
SWEAT CHLORIDE (pharmacodynamic measure)
Treatment difference through:
24 weeksa
−54 mmol/L (95% CI: -62, -47; P<0.0001)
48 weeksa
−53 mmol/L (95% CI: -61, -46; P<0.0001)
- There was no direct correlation between decrease in sweat chloride levels and improvement in lung function (FEV1)1
aTreatment difference = effect of KALYDECO – effect of placebo.1
The risk of pulmonary exacerbations was not analyzed in Trial 2 due to low incidence of events.1
TRIAL 4 (KONNECTION): Patients with CF age 6 years and older. KALYDECO® (ivacaftor): Significant improvements demonstrated for the overall population with eligible mutations1,2
ON THIS PAGE: Study Design | Summary of Results
Mutations Eligible for Study1 (mutations in bold were enrolled)
G1244E, G1349D, G178R, G551S, G970R*, S1251N, S1255P, S549N, or S549R
*KALYDECO is not indicated for use in patients with a G970R mutation
*Based on the clinical and pharmacodynamic (sweat chloride) responses to ivacaftor, efficacy in patients with the G970R mutation could not be established.
STUDY DESIGN1
- Trial 4 was a Phase 3, two-part, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover-design trial (two 8-week treatment periods separated by a 4- to 8-week washout period; N=39) in patients with CF age 6 years and older (mean age: 23 years)
- Patients had either a G1244E, G1349D, G178R, G551S, G970R, S1251N, S1255P, S549N, or S549R mutation
- Patients had to have FEV1 ≥40% predicted at screening [mean FEV1 78% predicted at baseline (range: 43%-119%)]
- Patients received KALYDECO 150 mg or placebo every 12 hours with fat-containing food, in addition to their prescribed CF therapies
Primary endpoint1: Improvement in lung function as determined by the mean absolute change from baseline in ppFEV1 through 8 weeks
Other endpoints1: Absolute change from baseline in: BMI at 8 weeks, improvement in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score through 8 weeks, and sweat chloride concentration through 8 weeks
SUMMARY OF RESULTS2
Significant improvements in ppFEV1 were maintained through 8 weeks of treatment2
There was a high degree of variability of efficacy responses among the 9 mutations studied1
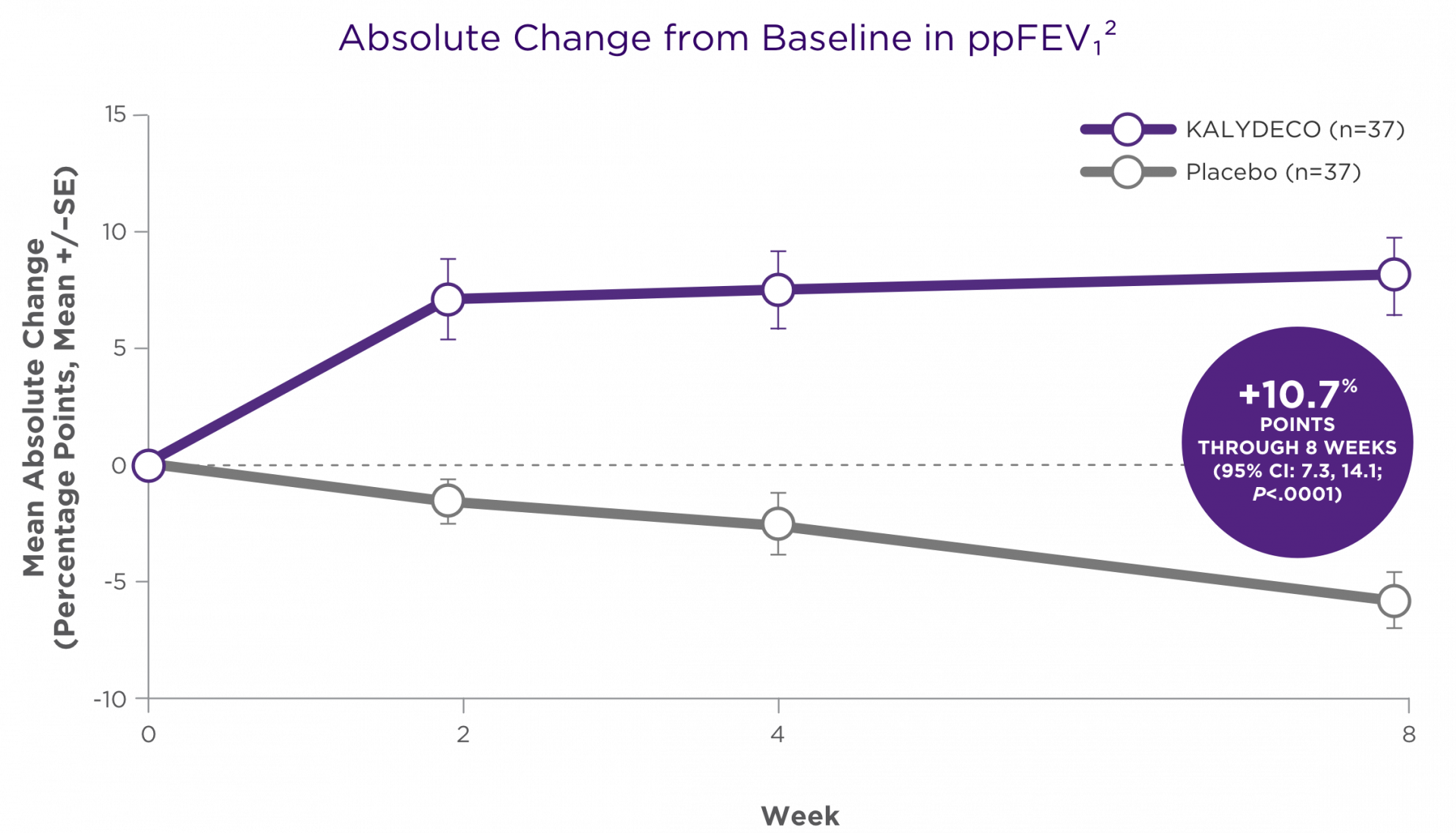
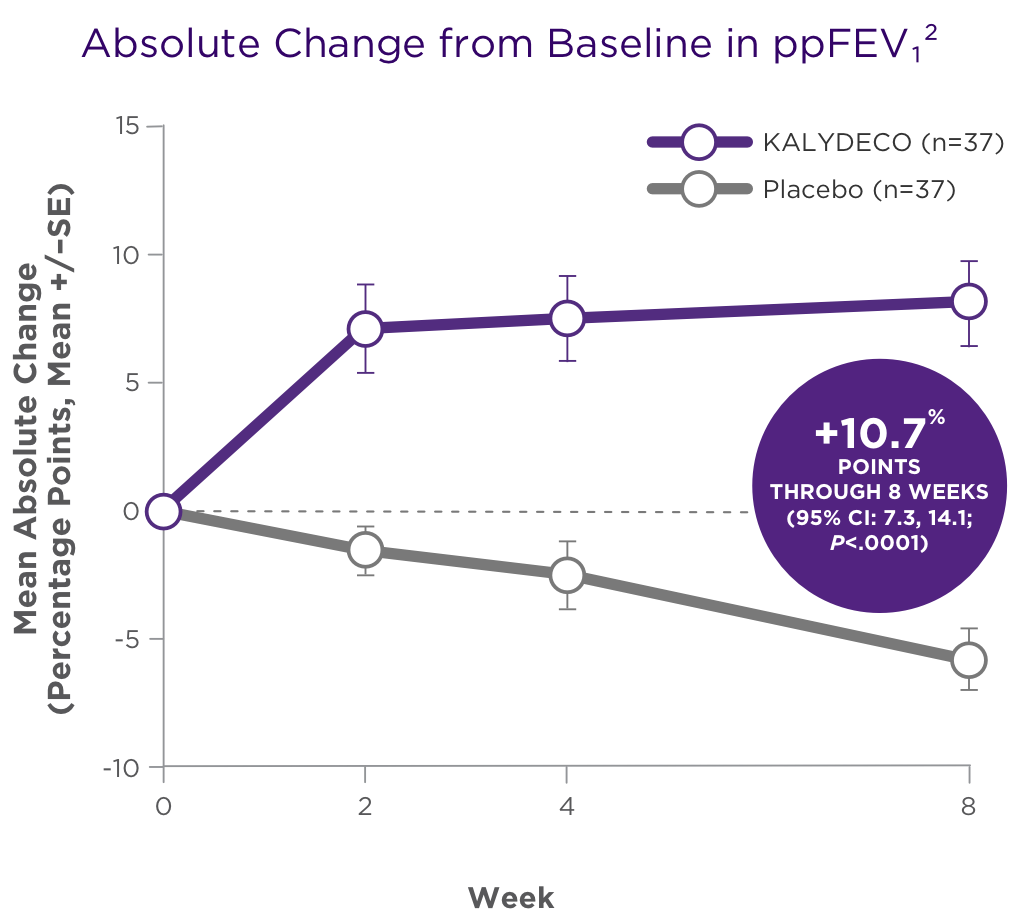
Adapted with permission from De Boeck K et al. J Cyst Fibros. 2014;13:674-680.
- For individual mutations, mean increases in ppFEV1 ranged from +3% points to +20% points at Week 81
- Based on the clinical and pharmacodynamic (sweat chloride) responses to ivacaftor, efficacy in patients with the G970R mutation could not be established1
There was a high degree of variability of responses among the 9 mutations studied1,2
BMI
Treatment difference at 8 weeksa
+0.66 kg/m2
(95% CI: 0.34, 0.99; P<0.0001)
- Mean increases ranged from
+0.16 kg/m2 to +1.62 kg/m2 at Week 8
CFQ-R RESPIRATORY DOMAIN SCORE
Treatment difference through 8 weeksa
+9.6 points
(95% CI: 4.5, 14.7; P=0.0004)
- CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score evaluated relevant CF respiratory symptoms including cough, sputum production, and difficulty breathing
- Mean increases ranged from +1.4 points to +23.3 points at Week 8
SWEAT CHLORIDE1,2
Treatment difference through 8 weeksa
−49 mmol/L
(95% CI: -57, -41; P<0.0001)
- There was no direct correlation between decrease in sweat chloride levels and improvement in lung function (FEV1)
- Reductions ranged from -80 mmol/L to -6 mmol/L at Week 8
aTreatment difference = effect of KALYDECO – effect of placebo.1
*Reflects results from the 1 patient with the G551S mutation with data at the 8-week time point.
See the full Prescribing Information for complete results by mutation.
TRIAL 5 (KONDUCT): Patients with CF age 6 years and older.
Results with KALYDECO® (ivacaftor) in patients with the R117H mutation1,2
ON THIS PAGE: Study Design | Summary of Results
Mutation Eligible for Study1 (mutation in bold was enrolled)
R117H
STUDY DESIGN1
- Trial 5 was a 24-week, Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial in patients with CF age 6 years and older (mean age: 31 years) who had an R117H mutation
- Patients age 12 years and older had to have FEV1 40%-90% predicted at screening; patients age 6 to 11 years had to have FEV1 40%-105% predicted at screening; mean FEV1 73% predicted at baseline (range: 33%-106%)
- Patients received KALYDECO 150 mg or placebo every 12 hours with fat-containing food, in addition to their prescribed CF therapies
- Subgroups analyzed were based on age, lung function, and poly-T status
Primary endpoint1: Improvement in lung function as determined by the mean absolute change from baseline in ppFEV1 through 24 weeks
Other efficacy endpoints1: Absolute change in BMI at Week 24, CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score through Week 24, time to first pulmonary exacerbation, and absolute change in sweat chloride from baseline through Week 24
SUMMARY OF RESULTS1
Overall change in ppFEV1 through Week 24, 2.1 percentage points (N=69), was not statistically significant1
| Absolute Change in ppFEV1 Through Week 241,a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUBGROUP PARAMETER | TREATMENT ARM | n | MEAN | TREATMENT DIFFERENCE (95% CI) |
| R117H– all patients |
Placebo | 35 | 0.5 | 2.1 (-1.1, 5.4) |
| KALYDECO | 34 | 2.6 | ||
| SUBGROUP BY AGE (YEARS) | ||||
| 6-11 | Placebo | 8 | 3.5 | -6.3 (-12.0, -0.7) |
| KALYDECO | 9 | -2.8 | ||
| 2-17 | Placebo | 1 | - | - |
| KALYDECO | 1 | - | ||
| >18 | Placebo | 26 | -0.5 | 5.0 (1.1, 8.8) |
| KALYDECO | 24 | 4.5 | ||
| SUBGROUP BY POLY-T STATUSb | ||||
| 5T | Placebo | 24 | 0.7 | 5.3 (1.3, 9.3) |
| KALYDECO | 4 | 6.0 | ||
| 7T | Placebo | 5 | -0.9 | 0.2 (-8.1, 8.5) |
| KALYDECO | 11 | -0.7 | ||
| SUBGROUP BY BASELINE ppFEV1 | ||||
| <70% | Placebo | 15 | 0.4 | 4.0 (-2.1, 10.1) |
| KALYDECO | 13 | 4.5 | ||
| 70%–90% | Placebo | 14 | 0.2 | 2.6 (-2.3, 7.5) |
| KALYDECO | 14 | 2.8 | ||
| >90% | Placebo | 6 | 2.2 | -4.3 (-9.9, 1.3) |
| KALYDECO | 7 | -2.1 | ||
| Subgroup parameter | R117H– all patients |
|
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 35 | 34 |
| Mean | 0.5 | 2.6 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
2.1 (-11, 5.4) | |
| Subgroup parameter | 6-11 | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 8 | 9 |
| Mean | 3.5 | -2.8 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
-6.3 (-12.0, -0.7) | |
| Subgroup parameter | 12-17 | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 1 | 1 |
| Mean | - | - |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
- | |
| Subgroup parameter | >18 | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 26 | 1 |
| Mean | 24 | 4.5 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
5.0 (1.1, 8.8) | |
| Subgroup parameter | 5T | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 24 | 14 |
| Mean | 0.7 | 6.0 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
5.3 (1.3, 9.3) | |
| Subgroup parameter | 7T | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 5 | 11 |
| Mean | -0.9 | -0.7 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
0.2 (8.1, 8.5) | |
| Subgroup parameter | <70% | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 15 | 13 |
| Mean | 0.4 | 4.5 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
4.0 (-2.1, 10.1) | |
| Subgroup parameter | 70%-90% | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 14 | 14 |
| Mean | 0.2 | 2.8 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
2.6 (-2.3, 7.5) | |
| Subgroup parameter | >90% | |
| Treatment arm | Placebo | KALYDECO |
| n | 6 | 7 |
| Mean | 2.2 | -2.1 |
| Treatment Difference (95% Cl) |
-4.3 (-9.9, 1.3) | |
aMMRM analysis with fixed effects for treatment, age, week, baseline value, treatment by week, and subject as a random effect.
bPoly-T status confirmed by genotyping (n=54).
Results for other efficacy endpoints studied in Trial 51,2
BODY WEIGHT
Treatment difference at 24 weeksc
+0.3 kg/m2
(95% CI: −1.57, 2.10; not statistically significant)
CFQ-R RESPIRATORY DOMAIN SCORE
Treatment difference through 24 weeksc
+8.4 points
(95% CI: 2.2, 14.6; P=0.009*)
*p-values are nominal
- CFQ-R Respiratory Domain score evaluated relevant CF respiratory symptoms, including cough, sputum production, and difficulty breathing
- Results ranged from −6.1 to +15.3 points
RELATIVE RISK OF PULMONARY EXACERBATION
Treatment difference through 24 weeksc
7% reduction (HR, 0.93; not statistically significant)
SWEAT CHLORIDE (pharmacodynamic measure)
Treatment difference through 24 weeksc
−24 mmol/L
(95% CI: −28.0, -19.9; P<0.0001*)
*p-values are nominal
- There was no direct correlation between decrease in sweat chloride levels and improvement in lung function (FEV1)
- Reductions in sweat chloride were seen in all subgroups, and ranged from −27.6 mmol/L to −20.0 mmol/L
HR, hazard ratio; BMI, body mass index.
cTreatment difference = effect of KALYDECO – effect of placebo.1
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Transaminase (ALT or AST) Elevations
- Elevated transaminases have been reported in patients with CF receiving KALYDECO. Transaminase elevations were more common in patients with a history of transaminase elevations or in patients who had abnormal transaminases at baseline. ALT and AST should be assessed prior to initiating KALYDECO, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter. For patients with a history of transaminase elevations, consider more frequent monitoring of liver function tests
- Patients who develop increased transaminase levels should be closely monitored until the abnormalities resolve. Dosing should be interrupted in patients with ALT or AST of greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Following resolution of transaminase elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming KALYDECO
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KALYDECO is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients age 1 month and older who have at least one mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive to ivacaftor potentiation based on clinical and/or in vitro assay data.
If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of a CFTR mutation followed by verification with bi-directional sequencing when recommended by the mutation test instructions for use.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KALYDECO is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients age 1 month and older who have at least one mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive to ivacaftor potentiation based on clinical and/or in vitro assay data.
If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of a CFTR mutation followed by verification with bi-directional sequencing when recommended by the mutation test instructions for use.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Transaminase (ALT or AST) Elevations
- Elevated transaminases have been reported in patients with CF receiving KALYDECO. Transaminase elevations were more common in patients with a history of transaminase elevations or in patients who had abnormal transaminases at baseline. ALT and AST should be assessed prior to initiating KALYDECO, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter. For patients with a history of transaminase elevations, consider more frequent monitoring of liver function tests
- Patients who develop increased transaminase levels should be closely monitored until the abnormalities resolve. Dosing should be interrupted in patients with ALT or AST of greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Following resolution of transaminase elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming KALYDECO
Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing setting. If signs or symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions develop during treatment, discontinue KALYDECO and institute appropriate therapy. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with KALYDECO
Concomitant Use With CYP3A Inducers
- Use of KALYDECO with strong CYP3A inducers, such as rifampin, substantially decreases the exposure of ivacaftor, which may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of KALYDECO. Co-administration of KALYDECO with strong CYP3A inducers, such as rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John's wort is not recommended
Cataracts
- Cases of non-congenital lens opacities/cataracts have been reported in pediatric patients treated with KALYDECO. Baseline and follow-up ophthalmological examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating treatment with KALYDECO
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Serious adverse reactions, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, which occurred more frequently in patients treated with KALYDECO included abdominal pain, increased hepatic enzymes, and hypoglycemia
Most Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions in the 221 patients treated with KALYDECO were headache (17%), upper respiratory tract infection (16%), nasal congestion (16%), nausea (10%), rash (10%), rhinitis (6%), dizziness (5%), arthralgia (5%), and bacteria in sputum (5%)
- The safety profile for the CF patients enrolled in clinical trials (Trials 3-8) was similar to that observed in the 48-week, placebo-controlled trials (Trials 1 and 2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of KALYDECO in patients with CF younger than 1 month of age have not been established. The use of KALYDECO in children under the age of 1 month is not recommended
- Use of KALYDECO in patients aged 1 to less than 6 months born at a gestational age less than 37 weeks has not been evaluated
Click here to access full Prescribing Information.
References:
1. KALYDECO (ivacaftor) [prescribing information]. Boston, MA: Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated; August 2023. 2. Davies JC, Wainwright CE, Canny GJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of ivacaftor in patients aged 6 to 11 years with cystic fibrosis with G551D mutation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187(11):1219–1225.

